Plant, Cell and Environment 35: 1769-1786 (2012)
Molecular mechanisms of seed dormancy
University of Freiburg, Faculty of Biology, Institute for Biology II, Botany / Plant Physiology, Schänzlestr. 1, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany (KG, GLM)
Department of Plant Breeding & Genetics, Max Planck Institute for Plant Breeding Research, Carl-von-Linné-Weg 10, 50829 Cologne, Germany (KN, EM, WM)
School of Biological Sciences, Plant Molecular Science, Royal Holloway, University of London, Egham, Surrey TW20 0EX, Uk (GLM);
Web: 'The Seed Biology Place' - www.seedbiology.eu
*Equal contribution
Received 2012; Revised 2012; Accepted 2012
Article first published online: 19 June 2012
DOI 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2012.02542.x
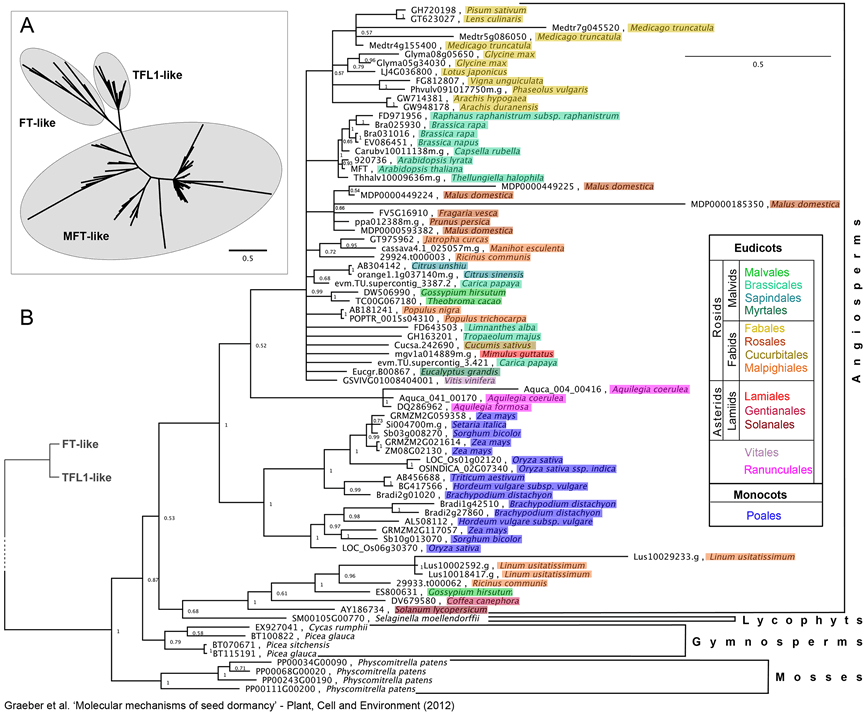
Figure 3. Phylogenetic analysis of MFT-like proteins.
(a) Unrooted Bayesian tree topology of plant PEBP proteins indicating the three main clades FT-like, TFL1-like and MFT-like.
(b) Detailed sub-tree of the MFT-like clade shown in (a) illustrating the broad phylogenetic distribution of MFT-like proteins among plants.
Given are sequence accession numbers/gene names (Phytozome, PLAZA, Genebank) and the respective species names. Angiosperm species are colour coded to the order level as indicated. Node labels depict posterior probabilities from the Bayesian inference analysis. Scale bar shows substitutions per site. Sequence data were obtained by querying comparative genomic databases Phytozome and PLAZA with Arabidopsis MFT sequence and combined with previously identified MFT-like sequences for species not included in these databases from Hedman et al. (2009), Karlgren et al. (2011) and Nakamura et al. (2011). This data set (Phytozome family #31632823, PLAZA orthogroup ortho002920 and literature derived MFT-like sequences) contained 99 sequences from 52 species. The deduced amino acid sequences were aligned together with Arabidopsis FT and TFL1 sequences [to be able to clearly identify MFT-like genes as depicted in (a)] using MUSCLE (Edgar 2004). Phylogenetic analysis by Bayesian Inference was performed using MrBayes 2.0.3 (Huelsenbeck & Ronquist 2001). Analysis was based on Jones rate matrix allowing heterogeneity between site (four gamma rate categories) and priors set to defaults. Two parallel Markov runs each with four heated chains starting from random trees were analysed for 1.5 million generations, sampling every 1000th generation disregarding the first 150 000 steps as burn in.
| Article in PDF format (1.2 MB) |
|
|
|
The Seed Biology Place |
Webdesign Gerhard Leubner 2000 |